8.1.8.3. KENO Sample Problems
This section contains sample problems to demonstrate some of the options available in KENO in stand-alone mode. Because stand-alone KENO has no means to read standard composition information and process for use, the problem-dependent cross section library must be prepared before executing KENO in the multigroup mode. The MIXTURE data block (See Sect. 8.1.3.1) is used to provide the mixing table. In the continuous energy mode, the cross sections are directly used and therefore no problem-dependent library is needed. The mixing table is required in the continuous energy mode as well. If KENO is executed as part of CSAS5 or CSAS6 sequence, generation of the problem-dependent library (for the multigroup mode) and the mixing table is automatically performed by the sequence.
A total of 33 KENO V.a different case inputs and 27 KENO-VI inputs are provided as multigroup mode KENO sample problems in a single input file “kenova.inp” and “kenovi.inp” for KENO V.a and KENO-VI, respectively. This input file contains an initial CSAS-MG input to create the problem-dependent cross section library to be used in the sample problems in the input file. Although KENO does not run stacked cases, when KENO is run as part of SCALE, the driver allows KENO to be executed each time it encounters an =KENOVA, respectively =KENOVI. The “.inp” file contains all 33/27 problems one after the other. A similar input file “cekenova.inp”, respectively “cekenovi.inp” is also provided for continuous energy mode of calculations. The changes required to create the continuous energy mode input file from the multigroup mode input file are simple. The continuous energy mode file does not have (or need) the CSAS-MG input at the beginning. In addition, all “lib=4” entries in the PARAMETER data block are changed to cep=ce_v7.1_endf to indicate the mode of calculation is continuous energy and the continuous energy cross section directory file is “ce_v7.1_endf” indicating ENDF/B-VII.1-based cross sections. The mixing table entry SCT is not applicable in the continuous energy mode, so it has been deleted from the continuous energy input file. Finally, material-specific albedos have also been removed from the continuous-energy input because they are not supported with continuous-energy mode.
The same 33/27 problems are also executed as individual cases with filenames “k5smp??.inp”, respectively “k6smp??.inp”, where ?? stands for sample problem number (01 through 33 or 27). Since each one of these sample problems needs a problem-dependent cross section library (multigroup mode only) and a mixing table, these problems have been converted to run as CSAS5/6 problems. Similar input files are also provided to be run in the continuous energy mode and the files are named “cek5smp??.inp”, respectively “cek6smp??.inp”, where ?? again stands for sample problem number (01 through 33 or 27). The change required to create the continuous energy mode inputs from the multigroup mode inputs is very simple: the cross-section library name is changed from “v7.1-252” to “ce_v7.1”.
In the following section the input for each case is listed assuming the multigroup mode of calculation in KENO. The KENO input is also listed in the file corresponding “.inp” file. The CSAS-MG input file for these cases is in the next section.
Warning
Some input might show differences in NPG, NSK and GEN parameters between multigroup and continuous energy input files.
8.1.8.3.1. CSAS-MG data
CSAS-MG can (1) be run alone with problem-dependent working library on logical Unit 4 saved for later use with the KENO sample problems, or (2) be placed in front of the KENO sample problems.
The CSAS-MG SCALE control module calculates the necessary resonance data required to create the problem-dependent AMPX working format library using SCALE standard composition input.
The multigroup mode KENO sample problem input data are independent of energy group structure. To use a different energy group structure, simply supply the desired master cross-section library name in the CSAS-MG or CSAS5/6 data. See XSProc, Standard Composition and CSAS5/6 chapters for additional information and examples. See the XSLib chapter for information about the master format cross-section libraries that are available in SCALE.
Data for CSAS-MG are provided to create a problem-dependent AMPX working format cross-section library suitable for use with the multigroup mode KENO sample problems. These data include all of the mixtures used in the KENO sample problems and will create an AMPX working format cross-section library with nuclide IDs matching those in the KENO sample problem mixing tables. This cross-section library is problem-specific and is not appropriate for use with other problems.
The CSAS-MG input data to produce an AMPX working format cross-section library for the multigroup mode KENO V.a sample problems are given below. Note that “kenovi.inp” also has its own CSAS-MG data which is identical to the below input with some minor updates in the comment lines.
=csas-mg
xsproc to prepare 252 group working format xsec lib for kenova smp prbs
v7.1-252
read composition
' uranium metal for smp prbs 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,19,22,23,24,25,26,27,28
uranium 1 den=18.76 1 300
92234 1
92235 93.2
92236 0.2
92238 5.6 end
' uranyl nitrate solution for smp prbs 12,18,19 spg=1.555
solution mix=2 rho[uo2(no3)2]=415 92235 92.6
92238 5.9
92234 1
92236 0.5
molar[hno3]=0.009783
density=? temperature=300 vol_frac=1
end solution
' uranium metal for smp prbs 13,14
uranium 3 den=18.69 1 300
92234 1
92235 93.2
92236 0.2
92238 5.6 end
' uranium metal for smp prb 15
uranium 4 den=18.794 1 300
92234 1.09
92235 97.67
92236 0.21
92238 1.03 end
' uranyl fluoride solution for smp prb 16
solution mix=5 rho[uo2f2]=578.7 92235 93.2
92238 6.8
density=? temperature=300 vol_frac=1
end solution
' borated uranyl fluoride solution for smp prb 16
solution mix=6 rho[uo2f2]=578.7 92235 93.2
92238 6.8
density=? temperature=300 vol_frac=1
end solution
boron 6 den=0.0266 1 300 end
' uranyl fluoride solution for smp prb 17
solution mix=7 rho[uo2f2]=133 92235 93
92238 7
density=? temperature=300 vol_frac=1
end solution
' uranyl fluoride solution for smp prb 20
solution mix=8 rho[uo2f2]=576.87 92235 93.2
92238 6.8
density=? temperature=300 vol_frac=1
end solution
' uranyl fluoride solution for smp prb 21 spg= 1.56
solution mix=9 rho[uo2f2]=494 92235 4.89
92238 95.09
92234 0.02
density=? temperature=300 vol_frac=1
end solution
' paraffin for smp prbs 3,4,18
paraffin 10 1 300 end
' plexiglas for smp prbs 12,15,18,19
plexiglas 11 1 300 end
' water for smp prbs 15
h2o 12 1 300 end
' pyrex glass for smp prb 16
pyrex 13 1 300 end
' aluminum for smp prb 20,21
al 14 1 300 end
' low density water for smp prb 18
h2o 15 1e-09 300 end
' uranium metal for smp prbs 29 - 32
uranium 16 den=18.747 1 300
92234 0.9844
92235 93.21
92236 0.0359
92238 5.7697 end
' uranium metal for water moderated portion of smp prb 33
uranium 17 den=19 1 300
92234 0.002
92235 1.95
92236 0.006
92238 98.042 end
' internal (2nd) moderator water for smp prb 33
h2o 18 1 300 end
' external moderator water and reflector for smp prb 33
h2o 19 1 300 end
' uranium metal for bare portion of smp prb 33
uranium 20 den=19 1 300
92234 0.002
92235 1.95
92236 0.006
92238 98.042 end
end composition
read celldata
'latticecell data for samp prb 33
latticecell atriangpitch imodr=3.302 18 fuelr=9.144 17 hpitch=10.414 19 end
latticecell atriangpitch imodr=3.302 0 fuelr=9.144 20 hpitch=10.414 0 end
end celldata
end
8.1.8.3.2. KENO V.a sample problem data
A brief problem description and the associated input data are included for each multigroup mode KENO sample problems. Different options may be easily activated by making changes in the data. These problems are set up using an AMPX working format library which was created by a CSAS-MG case just prior to the KENO V.a/KENO-VI cases. The nuclide identifiers for this library are consistent with the SCALE identifiers created by CSAS-MG. Input data to create this library are given in Sect. 8.1.8.3.1. The unit number is defined by the parameter LIB= in the parameter data.
8.1.8.3.2.1. Sample Problem 1 2C8 BARE
This is a simple 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array of uranium metal cylinders as described in the article “Critical Three-Dimensional Arrays of U(93.2)-Metal Cylinders,” [KENO-Appendix-CTho73] by J. T. Thomas. This critical experiment is designated in Table II of that article as cylinder index 11 and reflector index 1. Fig. 8.1.233 shows the critical experiment.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 1 case 2c8 bare
read parameters
flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
end geometry
read array
nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
kenovi sample problem 1 case 2c8 bare
read parameters
flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=8938.968624
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=10710.044784
boundary 20
global unit 2
cuboid 10 4p13.74 2p13.01
com='2x2x2 2c8 array'
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 2r-6.87 -6.505
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
end data
end
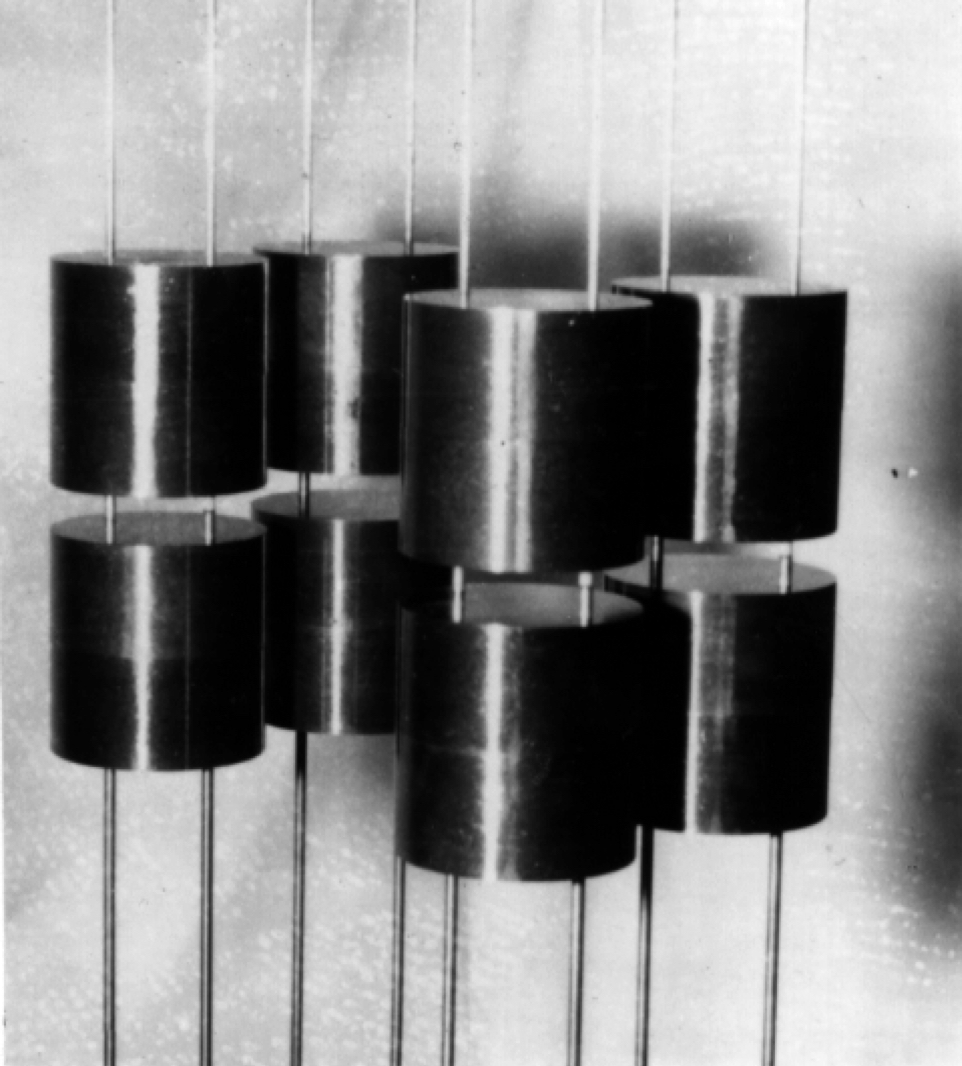
Fig. 8.1.233 Critical 2C8 bare assembly.
8.1.8.3.2.2. Sample Problem 2 CASE 2C8 BARE WITH 8 UNIT TYPES MATRIX CALCULATION
This problem is the same as sample problem 1 except it is set up as a mixed unit problem with each unit of the array defined as a different unit type. Matrix k-effectives will be calculated for this problem by both unit type and array position. The print flags are set to print all matrix data.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 2 2c8 bare with 8 unit types matrix calculation
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes
mku=yes fmu=yes mkp=yes fmp=yes
htm=no
end param
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 2
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 3
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 4
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 5
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 6
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 7
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 8
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
end geom
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read array
nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 loop
10*1
3*2 7*1
3 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1
4 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1
5 6*1 2 2 1
6 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 1
7 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 1
8 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 1 end loop
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
kenovi sample problem 2 case 2c8 bare with 8 unit types matrix cal
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes mku=yes cku=yes fmu=yes mkp=yes ckp=yes fmp=yes
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
unit 2
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
unit 3
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
unit 4
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
unit 5
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
unit 6
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
unit 7
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
unit 8
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
global unit 9
cuboid 10 4p13.74 2p13.01
com='2x2x2 2c8 array'
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 2r-6.87 -6.505
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 gbl=1
loop 10*1
3*2 7*1
3 1 1 1 2 2 1 1 1 1
4 2 2 1 2 2 1 1 1 1
5 6*1 2 2 1
6 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 2 1
7 1 1 1 2 2 1 2 2 1
8 2 2 1 2 2 1 2 2 1 end loop
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.3. Sample Problem 3 2C8 15.24-CM PARAFFIN REFL
A 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array of uranium metal cylinders is reflected by 6 in. of paraffin on all faces (Fig. 8.1.233). This critical experiment1 is designated as cylinder index 11 and reflector index 5 in Table II of Ref. 1. Fig. 8.1.234 shows half of the critical experiment, which consisted of the half shown and the mirror image of it. These two assemblies were moved together to achieve criticality. The top reflector is missing in Fig. 8.1.234, but was present when criticality was achieved.
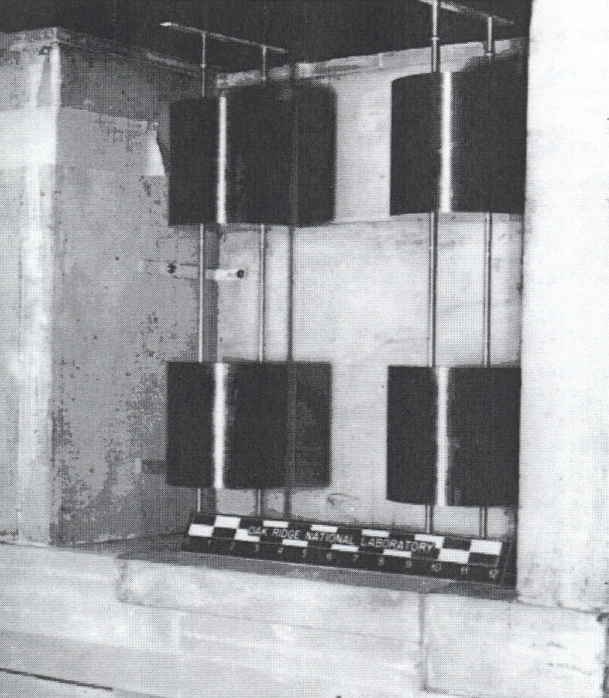
Fig. 8.1.234 Half of the paraffin reflected 2C8 assembly before the top reflector was added.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 3 2c8 15.24 cm paraffin refl
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes pwt=yes
htm=no
end param
read array
nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
read mixt
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=10
6000 3.84193e-02 9001001 7.99120e-02
sct=2
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 11.74 -11.74 11.74 -11.74 11.375 -11.375
global unit 2
array 1 -23.48 -23.48 -22.75
cuboid 2 2 26.48 -26.48 26.48 -26.48 25.75 -25.75
cuboid 2 3 29.48 -29.48 29.48 -29.48 28.75 -28.75
cuboid 2 4 32.48 -32.48 32.48 -32.48 31.75 -31.75
cuboid 2 5 35.48 -35.48 35.48 -35.48 34.75 -34.75
cuboid 2 6 38.72 -38.72 38.72 -38.72 37.99 -37.99
end geom
read bias
id=400 2 6
end bias
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
keno-vi sample problem 3 2c8 15.24 cm paraffin refl
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes pwt=yes
htm=no gen=300 nsk=10 npg=2000
end param
read mixt
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=10
6000 3.84193e-02 9001001 7.99120e-02
sct=2
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p11.74 2p11.375
media 1 1 10 vol=8938.968624
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=10710.044784
boundary 20
global unit 2
com='2x2x2 2c8 array with reflector'
cuboid 10 4p23.48 2p22.75
cuboid 20 26.48 -26.48 26.48 -26.48 25.75 -25.75
cuboid 30 29.48 -29.48 29.48 -29.48 28.75 -28.75
cuboid 40 32.48 -32.48 32.48 -32.48 31.75 -31.75
cuboid 50 35.48 -35.48 35.48 -35.48 34.75 -34.75
cuboid 60 38.72 -38.72 38.72 -38.72 37.99 -37.99
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 2r-11.74 -11.375
media 2 2 -10 +20 vol=4.41067E+04
media 2 3 -20 +30 vol=5.54410E+04
media 2 4 -30 +40 vol=6.80712E+04
media 2 5 -40 +50 vol=8.19974E+04
media 2 6 60 -50 vol=1.05694E+05
boundary 60
end geometry
read bias
id=400 2 6
end bias
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.4. Sample Problem 4 2C8 15.24-CM PARAFFIN REFL AUTOMATIC REFL
This problem is the same as sample problem 3 except it is set up using more reflector regions.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 4 2c8 15.24 cm paraffin refl automatic refl
read param
pwt=yes lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes
htm=no
end param
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 11.74 -11.74 11.74 -11.74 11.375 -11.375
global unit 2
array 1 -23.48 -23.48 -22.75
reflector 2 2 6*3.0 5
reflector 2 7 6*.24 1
end geom
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=10
6000 3.84193e-02 9001001 7.99120e-02
end mixt
read arra
nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
read bias
id=400 2 7
end bias
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
keno-vi sample problem 4 2c8 15.24 cm paraffin refl
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes pwt=yes
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=10
6000 3.84193e-02 9001001 7.99120e-02
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p11.74 2p11.375
media 1 1 10
media 0 1 20 -10
boundary 20
global unit 2
com='2x2x2 2c8 array with reflector'
cuboid 10 4p23.48 2p22.75
cuboid 20 26.48 -26.48 26.48 -26.48 25.75 -25.75
cuboid 30 29.48 -29.48 29.48 -29.48 28.75 -28.75
cuboid 40 32.48 -32.48 32.48 -32.48 31.75 -31.75
cuboid 50 35.48 -35.48 35.48 -35.48 34.75 -34.75
cuboid 60 38.48 -38.48 38.48 -38.48 37.75 -37.75
cuboid 70 38.72 -38.72 38.72 -38.72 37.99 -37.99
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 2r-11.74 -11.375
media 2 2 -10 +20
media 2 3 -20 +30
media 2 4 -30 +40
media 2 5 -40 +50
media 2 6 60 -50
media 2 7 70 -60
boundary 70
end geometry
read volume
type=trace
end volume
read bias
id=400 2 7
end bias
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.5. Sample Problem 5 2C8 12-INCH PARAFFIN ALBEDO REFLECTOR
This problem is the same as samples problems 3 and 4 except the reflector is represented by a 12 in. paraffin albedo. Note the decrease in execution time when using an albedo reflector instead of doing actual tracking. Note also that k-effective is somewhat higher for this system, probably due to the small edge size of the system [KENO-Appendix-CWT69].
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 5 2c8 12 inch paraffin albedo reflector
read para
flx=yes far=yes gas=no fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end para
read array
nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
read mixt
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
sct=2
end mixt
read bounds
all=paraffin
end bounds
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 11.74 -11.74 11.74 -11.74 11.375 -11.375
end geom
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
kenovi sample problem 5 2c8 12 inch paraffin albedo reflector
read para
flx=yes far=yes gas=no fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end para
read mixt
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
sct=2
end mixt
read bounds
all=paraffin
end bounds
read geometry
unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p11.74 2p11.375
media 1 1 10
media 0 1 20 -10
boundary 20
global unit 2
cuboid 10 4p23.48 2p22.75
com='2x2x2 2c8 array'
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 2r-11.74 -11.375
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
read volume
type=random
end volume
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.6. Sample Problem 6 ONE 2C8 UNIT (SINGLE UNIT)
One of the 2C units1 is described and run as a single-unit problem, and its k-effective is calculated.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 6 one 2c8 unit (single unit)
read para
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no
htm=no
end para
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
end geometry
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
kenovi sample problem 6 one 2c8 unit (single unit)
read para
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no
htm=no
end para
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.3710776
boundary 10
end geometry
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.7. Sample Problem 7 BARE 2C8 USING SPECULAR REFLECTION
One of the 2C units1 is described and the 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array is simulated by using specular reflection on the positive X, Y, and Z faces of the unit. This is a simulation of sample problem 1.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 7 bare 2c8 using specular reflection
read para
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
end geom
read bounds
+fc=specular
end bounds
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
keno-vi sample problem 7 bare 2c8 using specular reflection
read para
flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
end geometry
read bounds
+fc=specular
end bounds
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.8. Sample Problem 8 INFINITELY LONG CYLINDER FROM 2C8 UNIT
The fuel and cylinder radius from sample problem 1 is used. The length of the cylinder is arbitrarily chosen to be 20 cm, and the unit is specularly reflected on the top and bottom to create an infinitely long cylinder.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 8 infinitely long cylinder from 2c8 unit
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 10.0 -10.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 10.0 -10.0
end geometry
read bounds
zfc=mirror
end bounds
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
keno-vi sample problem 8 infinitely long cylinder from 2c8 unit
read parameters
lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 2p10.0
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p10.0
media 1 1 10
media 0 1 20 -10
boundary 20
end geometry
read bounds
zfc=mirror
end bounds
read volume
type=trace iface=zface
end volume
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.9. Sample Problem 9 INFINITE ARRAY OF 2C8 UNITS
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 9 infinite array of 2c8 units
read param
lib=4 gen=103
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read boun
all=mir
end boun
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
end geom
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
keno-vi sample problem 9 infinite array of 2c8 units
read parameters
lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=1338.755598
boundary 20
end geometry
read bounds
all=mirror
end bounds
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.10. Sample Problem 10 2C8 BARE WRITE RESTART
The geometry description from sample problem 1 is used, and the cuboid is specularly reflected on all faces to create an infinite array of 2C8 units having an edge-to-edge spacing of 2.244 cm in the X and Y directions and 2.245 cm in the Z direction.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 10 case 2c8 bare write restart
read parameters
flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no lib=4 res=5 wrs=94
app=yes
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
end geometry
read array
nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 10 case 2c8 bare write restart
read parameters
flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no lib=4 res=5 wrs=94 app=yes
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='single 2c8 unit centered'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.87 2p6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=8938.968624
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=10710.044784
boundary 20
global unit 2
cuboid 10 4p13.74 2p13.01
com='2x2x2 2c8 array'
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 2r-6.87 -6.505
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.11. Sample Problem 11 2C8 BARE READ RESTART DATA
This problem is a restart of sample problem 10. The problem is restarted from the tenth set of restart data that was written by sample problem 10 (i.e., it restarts with the fifty-first generation).
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 11 2c8 bare read restart data
read param
beg=51 rst=94 res=0
htm=no
end param
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 11 2c8 bare read restart data
read param
beg=51 rst=94 res=0
htm=no
end param
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.12. Sample Problem 12 4 AQUEOUS 4 METAL
This problem is a critical experiment consisting of a composite array1 of four highly enriched uranium metal cylinders and four cylindrical Plexiglas containers filled with uranyl nitrate solution. The metal units in this experiment are designated in Table II of Ref. 1 as cylinder index 11 and reflector index 1. A photograph of the experiment is given in Fig. 8.1.235.
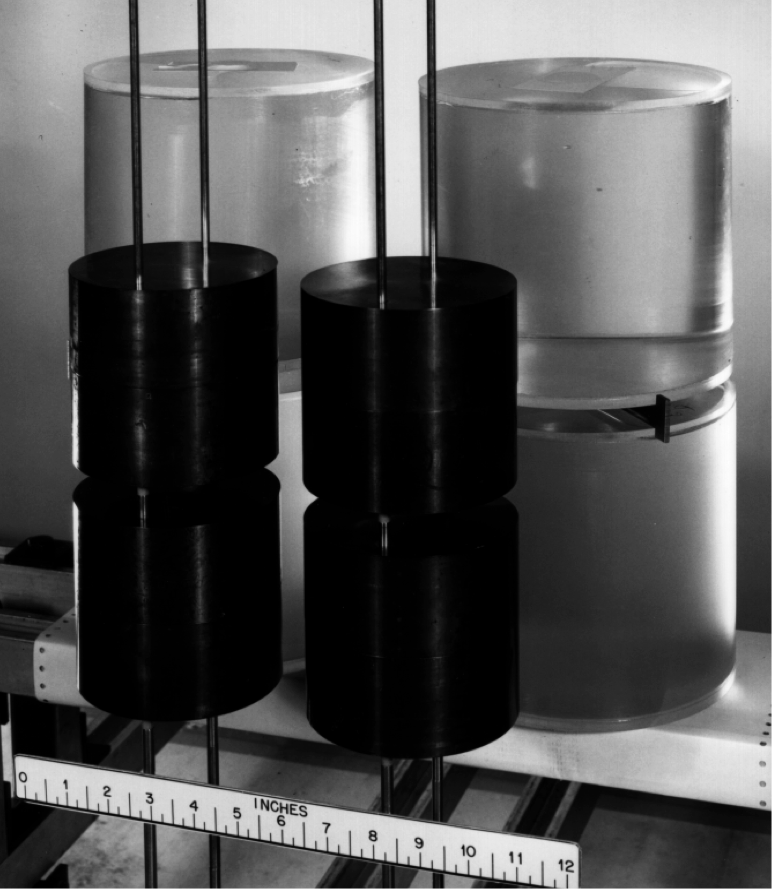

Fig. 8.1.235 Critical assembly of 4 solution units and 4 metal units.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 12 4 aqueous 4 metal mixed units
read param
lib=4 fdn=yes nub=yes smu=yes mkp=yes
mku=yes fmp=yes fmu=yes
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=2
1001 5.77931e-02 7014 2.13092e-03 8016 3.74114e-02
92234 1.06784e-05 92235 9.84602e-04 92236 5.29386e-06
92238 6.19414e-05
mix=3 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 2 1 9.525 8.89 -8.89
cylinder 3 1 10.16 9.525 -9.525
cuboid 0 1 10.875 -10.875 10.875 -10.875 10.24 -10.24
unit 2
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.59 -15.16 6.59 -15.16 6.225 -14.255
unit 3
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.59 -15.16 15.16 -6.59 6.225 -14.255
unit 4
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.59 -15.16 6.59 -15.16 14.255 -6.225
unit 5
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.59 -15.16 15.16 -6.59 14.255 -6.225
end geom
read array
gbl=1 ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 loop
1 3r2 1 2 1 1 2 1
2 9r1
3 3r1 2 2 1 3r1
4 6r1 2 2 1
5 3r1 2 2 1 2 2 1 end loop
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 12 4 aqueous 4 metal mixed units
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes nub=yes smu=yes mku=yes fmp=yes fmu=yes
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=2
1001 5.77931e-02 7014 2.13092e-03 8016 3.74114e-02
92234 1.06784e-05 92235 9.84602e-04 92236 5.29386e-06
92238 6.19414e-05
mix=3 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 10 9.525 8.89 -8.89
cylinder 20 10.16 9.525 -9.525
cuboid 30 10.875 -10.875 10.875 -10.875 10.24 -10.24
media 2 1 10 vol=20270.8327
media 3 1 -10 20 vol=4440.27764
media 0 1 30 -20 vol=14042.16966
boundary 30
unit 2
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 6.59 -15.16 6.59 -15.16 6.225 -14.255
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=8570.948922
boundary 20
unit 3
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 6.59 -15.16 15.16 -6.59 6.225 -14.255
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=8570.948922
boundary 20
unit 4
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 6.59 -15.16 6.59 -15.16 14.255 -6.225
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=8570.948922
boundary 20
unit 5
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 20 6.59 -15.16 15.16 -6.59 14.255 -6.225
media 1 1 10 vol=1117.371078
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=8570.948922
boundary 20
global
unit 6
cuboid 10 43.5 0.0 43.5 0.0 40.96 0.0
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 15.16 15.16 14.255
boundary 10
end geom
read array
gbl=1 ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 loop
1 3r2 1 2 1 1 2 1
2 9r1
3 3r1 2 2 1 3r1
4 6r1 2 2 1
5 3r1 2 2 1 2 2 1 end loop
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.13. Sample Problem 13 TWO CUBOIDS IN A CYLINDRICAL ANNULUS
This critical experiment [KENO-Appendix-CIM64] consists of two assemblies of 93.2% 235U-enriched uranium metal \((\rho=18.69 \mathrm{^g} / \mathrm{cc})\) stacked vertically. The bottom assembly contains a uranium metal cuboid offset to the left within a uranium metal cylindrical annulus. The top assembly contains a uranium metal cuboid offset to the right within a uranium metal cylindrical annulus. The cuboid extends above the annulus. A drawing of the two sections and the total assembly is given in Fig. 8.1.236.
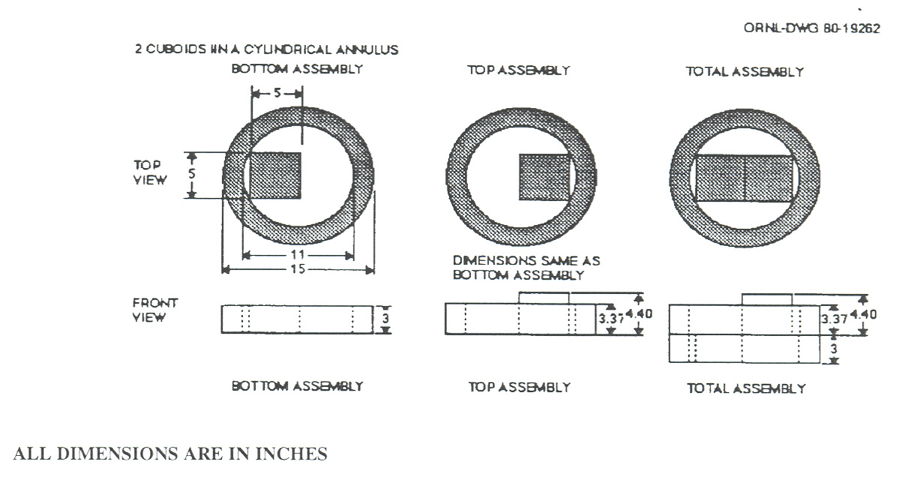
Fig. 8.1.236 Drawing of two cuboids in an annulus critical assembly.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 13 two cuboids in a cylindrical annulus
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read geom
unit 1
cuboid 1 1 6.35 -6.35 6.35 -6.35 7.62 0.0
cylinder 0 1 13.97 7.62 0.0 orig -6.0934 0.0
cylinder 1 1 19.05 7.62 0.0 orig -6.0934 0.0
cuboid 0 1 12.9566 -25.1434 19.05 -19.05 7.62 0.0
unit 2
cuboid 1 1 6.35 -6.35 6.35 -6.35 8.56 0.0
cylinder 0 1 13.97 8.56 0.0 origin 6.0934 0.0
cylinder 1 1 19.05 8.56 0.0 origin 6.0934 0.0
cuboid 0 1 25.1434 -12.9566 19.05 -19.05 8.56 0.0
unit 3
cuboid 1 1 6.35 -6.35 6.35 -6.35 2.616 0.0
cuboid 0 1 25.1434 -12.9566 19.05 -19.05 2.616 0.0
end geom
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=3
92234 4.80916e-04 92235 4.46300e-02 92236 9.53661e-05 92238 2.64776e-03
end mixt
read array
gbl=1 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=3 fill 1 2 3 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 13 two cuboids in a cylindrical annulus
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=3
92234 4.80916e-04 92235 4.46300e-02 92236 9.53661e-05 92238 2.64776e-03
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
cuboid 10 6.35 -6.35 6.35 -6.35 7.62 0.0
cylinder 20 13.97 7.62 0.0 orig x=-6.0934
cylinder 30 19.05 7.62 0.0 orig x=-6.0934
cuboid 40 12.9566 -25.1434 19.05 -19.05 7.62 0.0
media 1 1 10 vol=1229.0298
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=3442.914497898
media 1 1 30 -20 vol=4015.555429598
media 0 1 40 -30 vol=2373.768472504
boundary 40
unit 2
cuboid 10 6.35 -6.35 6.35 -6.35 8.56 0.0
cylinder 20 13.97 8.56 0.0 origin x=6.0934
cylinder 30 19.05 8.56 0.0 origin x=6.0934
cuboid 40 25.1434 -12.9566 19.05 -19.05 8.56 0.0
media 1 1 10 vol=1380.6424
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=3867.630984515
media 1 1 30 -20 vol=4510.912661071
media 0 1 40 -30 vol=2666.595554414
boundary 40
unit 3
cuboid 10 6.35 -6.35 6.35 -6.35 2.616 0.0
cuboid 20 25.1434 -12.9566 19.05 -19.05 2.616 0.0
media 1 1 10 vol=421.93464
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=3375.47712
boundary 20
global unit 4
cuboid 10 12.9566 -25.1434 2p19.05 18.796 0.
array 1 10 place 1 1 1 3r0.
boundary 10
end geom
read array
ara=1 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=3 fill 1 2 3 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.14. Sample Problem 14 U METAL CYLINDER IN AN ANNULUS
This critical experiment3 consists of a 93.2 235U-enriched uranium metal cylinder within a cylindrical annulus of the same material as shown in Fig. 8.1.237. The uranium metal specification is identical to that used in sample problem 13.
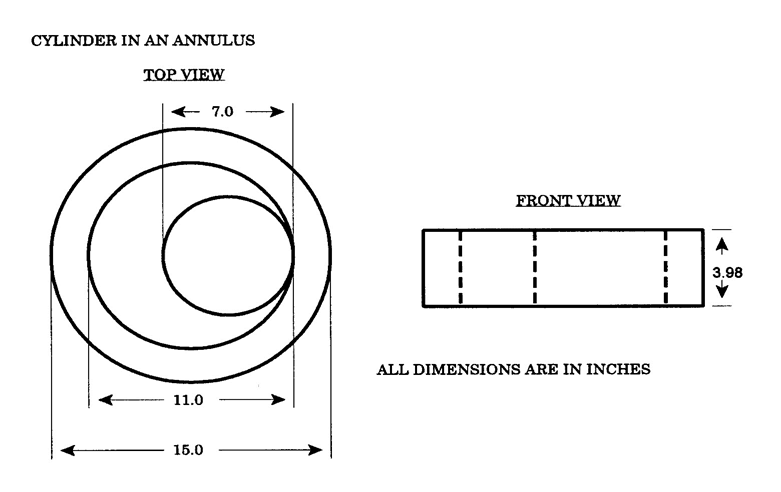
Fig. 8.1.237 Drawing of the cylinder in an annulus critical assembly.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 14 u metal cylinder in an annulus
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=3
92234 4.80916e-04 92235 4.46300e-02 92236 9.53661e-05 92238 2.64776e-03
end mixt
read geom
global unit 1
cylinder 1 1 8.89 10.109 0.0 orig 5.0799 0.0
cylinder 0 1 13.97 10.109 0.0
cylinder 1 1 19.05 10.109 0.0
end geom
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 14 u metal cylinder in an annulus
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=3
92234 4.80916e-04 92235 4.46300e-02 92236 9.53661e-05 92238 2.64776e-03
end mixt
read geom
global unit 1
cylinder 10 8.89 10.109 0.0 orig x=5.08
cylinder 20 13.97 10.109 0.0
cylinder 30 19.05 10.109 0.0
media 1 1 10 vol=2509.929894
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=3688.060252
media 1 1 30 -20 -10 vol=5327.198142
boundary 30
end geom
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.15. Sample Problem 15 SMALL WATER REFLECTED SPHERE ON PLEXIGLAS COLLAR
This critical experiment [KENO-Appendix-CBKH+77] is a small highly enriched uranium sphere supported by a Plexiglas doughnut in a tank of water. The sphere extends down through the hole of the doughnut. However, the KENO geometry package cannot rigorously describe a doughnut (torus) with either KENO V.a or KENO-VI. Therefore, the KENO mockup of this problem describes the doughnut as an annular cylindrical plate and the sphere is supported by it. Both are contained in a cylindrical tank of water. A drawing of the experiment is given in Fig. 8.1.238. This drawing shows the sphere above the cylindrical collar for the sake of clarity. The sphere is actually supported by the collar and extends into the opening in its center. The actual experiment utilized a torus or doughnut instead of a cylindrical collar.
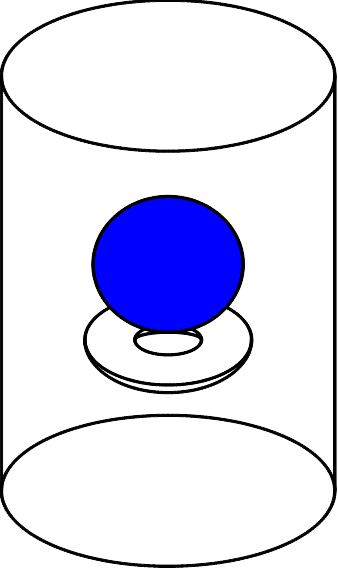
Fig. 8.1.238 Drawing of a critical assembly consisting of a uranium sphere on a Plexiglas collar with a cylindrical water reflector.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 15 small water reflected sphere on plexiglas collar
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=4
92234 5.27115e-04 92235 4.70308e-02 92236 1.00692e-04 92238 4.89708e-04
mix=2 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
mix=3 ncm=12
1001 6.67554e-02
mix=3 ncm=12
8016 3.33757e-02
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
hemisphe-z 1 1 6.5537 chord -5.09066
cylinder 3 1 4.1275 -5.09066 -7.63065
cylinder 2 1 12.7 -5.09066 -7.63065
cuboid 3 1 4p12.7 -5.09066 -7.63065
unit 2
hemisphe+z 1 1 6.5537 chord 5.09066
cuboid 3 1 4p12.7 6.5537 -5.09066
global unit 3
array 1 -12.7 -12.7 -7.092175
cylinder 3 1 17.97 2p7.0922
replicate 3 2 3*3.0 5
end geom
read bias
id=500 2 6
end bias
read array
nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 1 2 end fill
end array
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
ttl='x-z slice through the center of the sphere'
xul=-20.0 zul=10.0 yul=0.0 xlr=20.0 ylr=0.0 zlr=-10.0
uax=1.0 wdn=-1.0 nax=400
end plot
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 15 small water reflected sphere on plexiglas collar
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes plt=yes
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=4
92234 5.27115e-04 92235 4.70308e-02 92236 1.00692e-04 92238 4.89708e-04
mix=2 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
mix=3 ncm=12
1001 6.67554e-02
mix=3 ncm=12
8016 3.33757e-02
end mixt
read geom
global unit 1
sphere 10 6.5537
cylinder 20 4.1275 -5.09066 -7.63065
cylinder 30 12.7 -5.09066 -7.63065
cylinder 40 21.5537 21.5537 -21.5537
media 1 1 10 vol=1179.093598091
media 3 1 20 -10 vol=95.1516
media 2 1 30 -20 -10 vol=1151.089182028
media 3 1 40 -30 -20 -10 vol=60488.221616778
boundary 40
end geom
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
ttl='x-z slice through the center of the sphere'
xul=-20.0 zul=10.0 yul=0.0 xlr=20.0 ylr=0.0 zlr=-10.0
uax=1.0 wdn=-1.0 nax=400
end plot
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.16. Sample Problem 16 UO2F2 INFINITE SLAB K-INFINITY
This problem solves for the k-infinity of an infinite number of slabs of uranyl fluoride solution contained in Pyrex glass and separated by borated uranyl fluoride solution. The uranyl fluoride slab is 4.958 cm thick, 93.2% enriched, and has a density of 578.7 g U/l. The Pyrex glass is 1.27 cm thick and is present on both faces of the uranyl fluoride solution. A total of 27.46 cm of borated solution separates the Pyrex glass of adjacent slabs of solution. 1.482 \(\times\) 10-27 atoms of boron per milliliter are present in the borated solution.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 16 uo2f2 infinite slab k-infinity
read parameters
lib=4 amx=yes xap=no
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=5
9019 2.96287e-03 1001 6.08125e-02 8016 3.33691e-02 92235 1.38188e-03 92238 9.95505e-05
mix=2 ncm=13
11023 2.39503e-03 13027 4.97720e-04 14028 1.66260E-02 14029 8.41845E-04 14030 5.58826E-04
5010 9.14627e-04 5011 3.68149e-03 8016 4.49174e-02
mix=3 ncm=6
9019 2.96287e-03 1001 6.08125e-02 8016 3.33691e-02 92235 1.38188e-03 92238 9.95505e-05
5010 2.94862e-04 5011 1.18686e-03
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
cuboid 1 1 2.479 -2.479 100 -100 100 -100
cuboid 2 1 3.749 -3.749 100 -100 100 -100
cuboid 3 1 17.479 -17.479 100 -100 100 -100
end geom
read bounds
all=mirror
end bounds
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 16 uo2f2 infinite slab k-infinity
read parameters
lib=4 amx=yes xap=no
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=5
9019 2.96287e-03 1001 6.08125e-02 8016 3.33691e-02 92235 1.38188e-03 92238 9.95505e-05
mix=2 ncm=13
11023 2.39503e-03 13027 4.97720e-04 14028 1.66260E-02 14029 8.41845E-04 14030 5.58826E-04
5010 9.14627e-04 5011 3.68149e-03 8016 4.49174e-02
mix=3 ncm=6
9019 2.96287e-03 1001 6.08125e-02 8016 3.33691e-02 92235 1.38188e-03 92238 9.95505e-05
5010 2.94862e-04 5011 1.18686e-03
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
cuboid 10 2.479 -2.479 100.0 -100.0 100.0 -100.0
cuboid 20 3.749 -3.749 100.0 -100.0 100.0 -100.0
cuboid 30 17.479 -17.479 100.0 -100.0 100.0 -100.0
media 1 1 10
media 2 1 20 -10
media 3 1 30 -20 -10
boundary 30
end geom
read bounds
all=mirror
end bounds
read volume
type=trace iface=xface
end volume
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.17. Sample Problem 17 93% UO2F2 SOLUTION SPHERE ADJOINT CALCULATION
A single 93% enriched uranyl fluoride sphere is run as an adjoint calculation. The result for the forward and adjoint k-effectives should be the same within statistical error when the problem is run both ways.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 17 93% uo2f2 solution sphere adjoint calculation
read parameters
lib=4 npg=10000 nbk=10500 adj=yes amx=yes xap=no
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=7
1001 6.55892e-02 8016 3.34755e-02 9019 6.80925e-04 92235 3.16910e-04 92238 2.35522e-05
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
sphere 1 1 16.0
end geom
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 17 93% uo2f2 solution sphere adjoint calculation
read parameters
lib=4 amx=yes pwt=yes xap=no adj=yes npg=10000 nbk=10500 tba=0.5
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=7
1001 6.55892e-02 8016 3.34755e-02 9019 6.80925e-04 92235 3.16910e-04 92238 2.35522e-05
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
sphere 10 16.0
media 1 1 10 vol=17157.284678
boundary 10
end geom
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.18. Sample Problem 18 1F27 DEMONSTRATION OF OPTIONS
A reflected cubic array of 27 cylinders of aqueous uranyl nitrate in Plexiglas bottles [KENO-Appendix-CTho64]. The walls of the bottles were 0.64-cm thick, and each bottle was filled with 5 liters of 92.6% enriched solution at a concentration of 415 g/L, a specific gravity of 1.555 and 0.39 mg excess nitrate/g soln (From experimental facility documents. Not reported in ORNL/TM-719.) The 3 \(\times\) 3 \(\times\) 3 array was surrounded by a 6-in. paraffin reflector. Most of the print options available in KENO are exercised in this problem. A perspective of this critical experiment is shown in Fig. 8.1.239. A photograph of one of the experiments utilized 27 of the Plexiglas bottles is shown in Fig. 8.1.240. Sample problem 18 has 15.24 cm of paraffin on all six faces rather than the 2.54-cm Plexiglas shown on five faces.
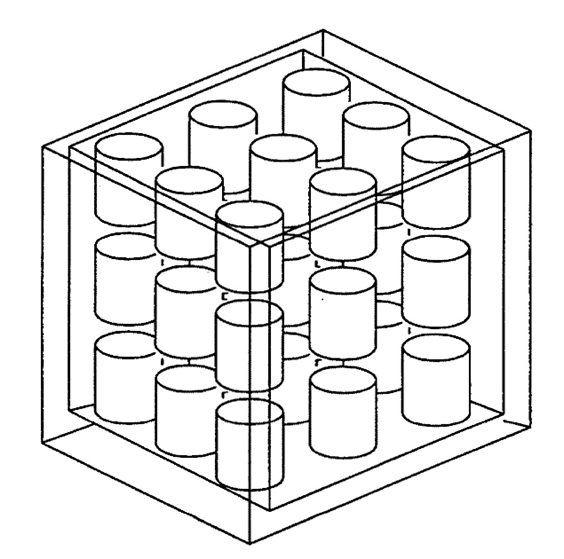
Fig. 8.1.239 Perspective of critical 1F27 experiment.
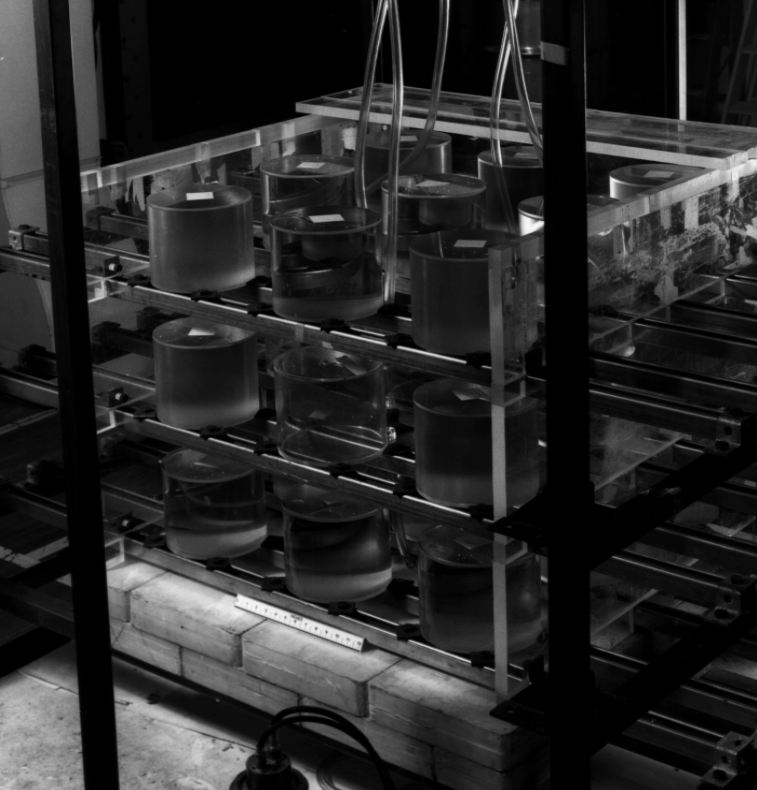

Fig. 8.1.240 View of a 27-unit array with 2.54-cm. thick Plexiglas reflector on five sides and a 15.24-cm. thick paraffin base.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 18 1f27 demonstration of options problem
read para gen=103 npg=1000 fdn=yes nub=yes lib=4
mku=yes fmu=yes mkh=yes fmh=yes mka=yes fma=yes rnd=f12c09ed2195
pwt=yes far=yes flx=yes amx=yes pax=yes pgm=yes
htm=no
end para
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=2
1001 5.77931e-02 7014 2.13092e-03 8016 3.74114e-02
92234 1.06784e-05 92235 9.84602e-04 92236 5.29386e-06
92238 6.19414e-05
mix=2 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
mix=3 ncm=10
6000 3.84193e-02 9001001 7.99120e-02
mix=4 ncm=15
8016 3.33757e-11 1001 6.67515e-11
end mixt
read bounds
-zb= h2o
end bounds
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 9.52 8.7804 -8.7804
cylinder 0 1 9.52 8.9896 -8.7804
cylinder 2 1 10.16 9.6296 -9.4204
cuboid 4 1 18.45 -18.45 18.45 -18.45 17.8946 -17.6854
unit 2
array 1 3*0.0
unit 3
array 2 3*0.0
unit 4
array 3 3*0.0
unit 5
array 4 3*0.0
global
unit 6
cuboid 4 1 55.3501 -55.3501 55.3501 -55.3501 53.3701 -53.3701
hole 2 -55.35 -18.45 -17.79
hole 3 -55.35 -18.45 -53.3701
hole 4 18.4501 -18.45 -53.3701
hole 5 -55.3501 -55.3501 -53.3701
replicate 3 2 6*3 5
replicate 3 7 6*0.24 1
end geom
read bias
id=400 2 7
end bias
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill f1 end fill
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=3 fill f1 end fill
ara=4 nux=3 nuy=1 nuz=3 fill f1 end fill
end array
read start
nst=6 tfx=0.0 tfy=0.0 tfz=0.0
lnu=1000 ps6=yes
end start
read plot
scr=yes plt=yes lpi=10
ttl=' 1f27 xy plot at z=0.0'
xul=-71.0 yul= 71.0 zul=0.0
xlr= 71.0 ylr=-71.0 zlr=0.0
uax=1 vdn=-1 nax=400
run=yes
end plt1
ttl='unit map 1f27 xy plot at z=0.0'
pic=unit
end plot
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 18 1f27 critical experiment
read para
gen=103 npg=1000 fdn=yes nub=yes lib=4 plt=yes
mku=yes cku=yes fmu=yes fmh=yes mka=yes cka=yes fma=yes pwt=yes
far=yes flx=yes amx=yes pax=yes pgm=yes rnd=f12c09ed2195
htm=no
end para
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=2
1001 5.77931e-02 7014 2.13092e-03 8016 3.74114e-02
92234 1.06784e-05 92235 9.84602e-04 92236 5.29386e-06
92238 6.19414e-05
mix=2 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
mix=3 ncm=10
6000 3.84193e-02 9001001 7.99120e-02
mix=4 ncm=15
8016 3.33757e-11 1001 6.67515e-11
end mixt
read bounds
-zb=h2o
end bounds
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 10 9.52 8.7804 -8.7804
cylinder 20 9.52 8.9896 -8.7804
cylinder 30 10.16 9.6296 -9.4204
cuboid 40 18.45 -18.45 18.45 -18.45 17.8946 -17.6854
media 1 1 10
media 0 1 -10 20
media 2 1 -10 -20 30
media 0 1 40 -20 -30
boundary 40
unit 2
cuboid 10 18.45 -55.35 55.35 -18.45 53.37 -17.79
cuboid 20 18.45 -55.35 55.35 -18.45 -17.79 -53.37
cuboid 30 55.35 18.45 55.35 -18.45 53.37 -53.37
cuboid 40 55.35 -55.35 -18.45 -55.35 53.37 -53.37
cuboid 50 55.35 -55.35 55.35 -55.35 53.37 -53.37
array 1 10 place 1 1 1 -36.90 0.0 -0.1046
array 2 20 -10 place 1 1 1 -36.90 0.0 -35.6846
array 3 30 -20 -10 place 1 1 1 36.90 0.0 -35.6846
array 4 40 -30 -20 -10 place 1 1 1 -36.90 -36.90 -35.6846
media 0 1 50 -40 -30 -20 -10
boundary 50
global unit 3
cuboid 10 55.35 -55.35 55.35 -55.35 53.37 -53.37
cuboid 20 58.35 -58.35 58.35 -58.35 56.37 -56.37
cuboid 30 61.35 -61.35 61.35 -61.35 59.37 -59.37
cuboid 40 64.35 -64.35 64.35 -64.35 62.37 -62.37
cuboid 50 67.35 -67.35 67.35 -67.35 65.37 -65.37
cuboid 60 70.59 -70.59 70.59 -70.59 68.61 -68.61
array 5 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
media 3 2 -10 20
media 3 3 -20 30
media 3 4 -30 40
media 3 5 -40 50
media 3 6 60 -50
boundary 60
end geom
read bias
id=400 2 6
end bias
read volume
type=random
end volume
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill f1 end fill
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=3 fill f1 end fill
ara=4 nux=3 nuy=1 nuz=3 fill f1 end fill
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill f2 end fill
end array
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
ttl=' 1f27 xy plot at z=0.0 '
xul=-71.0 yul=71.0 zul=0.0 xlr=71.0 ylr=-71.0 zlr=0.0
uax=1 vdn=-1 nax=400 end plt0
ttl='unit map 1f27 xy plot at z=0.0'
pic=unit
end plot
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.19. Sample Problem 19 4 AQUEOUS 4 METAL ARRAY OF ARRAYS (SAMP PROB 12)
This critical experiment was described previously as SAMPLE PROBLEM 12. The input data given below utilize the array of arrays option. See Fig. 8.1.235.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 19 4 aqueous 4 metal array of arrays (samp prob 12)
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes nub=yes smu=yes mkp=yes
mku=yes fmp=yes fmu=yes
htm=no
end param
read mixt
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=2
1001 5.77931e-02 7014 2.13092e-03 8016 3.74114e-02
92234 1.06784e-05 92235 9.84602e-04 92236 5.29386e-06
92238 6.19414e-05
mix=3 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
sct=2
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
com='uranyl nitrate solution in a plexiglas container'
cylinder 2 1 9.525 2p8.89
cylinder 3 1 10.16 2p9.525
cuboid 0 1 4p10.875 2p10.24
unit 2
com='uranium metal cylinder'
cylinder 1 1 5.748 2p5.3825
cuboid 0 1 4p6.59 2p6.225
unit 3
com='1x2x2 array of solution units'
array 1 3*0.0
unit 4
com='1x2x2 array of metal units padded to match solution array'
array 2 3*0.0
replicate 0 1 2*0.0 2*8.57 2*8.03 1
end geom
read array
ara=1 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
ara=2 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f2 end fill
gbl=3 ara=3 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1
com='composite array of solution and metal units'
fill 4 3 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 19 4 aqueous 4 metal array of arrays (samp prob 12)
read param
lib=4 flx=yes fdn=yes nub=yes smu=yes mkp=yes mku=yes fmp=yes fmu=yes
htm=no
end param
read mixt
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
mix=2 ncm=2
1001 5.77931e-02 7014 2.13092e-03 8016 3.74114e-02
92234 1.06784e-05 92235 9.84602e-04 92236 5.29386e-06
92238 6.19414e-05
mix=3 ncm=11
1001 5.67873e-02 6000 3.54921e-02 8016 1.41968e-02
sct=2
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='uranyl nitrate solution in a plexiglas container'
cylinder 10 9.525 2p8.89
cylinder 20 10.16 2p9.525
cuboid 30 4p10.875 2p10.24
media 2 1 10 vol=20270.83270
media 3 1 -10 20 vol=4440.27764
media 0 1 30 -20 vol=14042.16966
boundary 30
unit 2
com='uranium metal cylinder'
cylinder 10 5.748 2p5.3825
cuboid 20 4p6.59 2p6.225
media 1 1 10 vol=4469.48431
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=4181.39321
boundary 20
unit 3
com='1x2x2 array of solution units'
cuboid 10 21.75 0.0 43.5 0.0 40.96 0.0
array 1 +10 place 1 1 1 10.875 10.875 10.240
boundary 10
unit 4
com='1x2x2 array of metal units padded to match solution array'
cuboid 10 13.18 0.0 26.36 0.0 24.9 0.0
cuboid 20 13.18 0.0 34.93 -8.57 32.93 -8.03
array 2 +10 place 1 1 1 6.59 6.59 6.225
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=14830.750188
boundary 20
global unit 5
com='global unit of arrays 1 and 2'
cuboid 10 34.93 0.0 43.5 0.0 40.96 0.0
array 3 +10 place 1 1 1 0 8.57 8.03
boundary 10
end geom
read array
ara=1 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f1 end fill
ara=2 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f2 end fill
gbl=3 ara=3 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1
com='composite array of solution and metal units'
fill 4 3 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.20. Sample Problem 20 TRIANGULAR PITCHED ARRAY
This problem is a critical experiment14 consisting of seven cylinders in a triangular-pitched unreflected array. The central cylinder has six cylinders arranged around it. The surface-to-surface separation between the units is 0.15 in. Each unit consists of a 60-mil-thick aluminum can with an 8-in. inside diameter, filled with a solution of 93.2% enriched uranyl fluoride with a H/235U atomic ratio of 44.3 and a density of 576.87 g U/L. The apparatus for conducting this experiment is shown in Fig. 8.1.241.
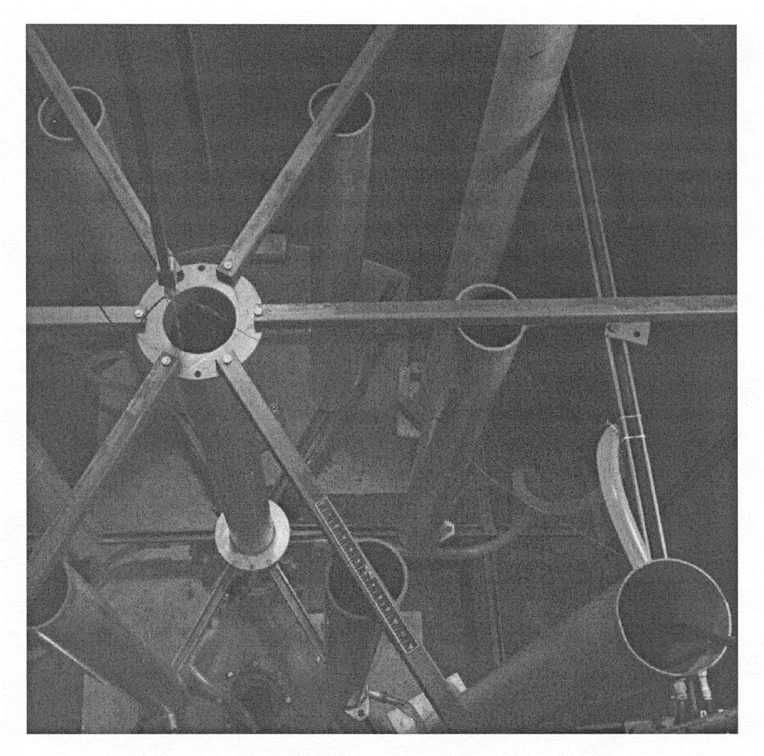
Fig. 8.1.241 Typical arrangement for critical experiments with interacting arrays of aluminum cylinders containing enriched 235U solutions.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 20 triangular pitched array
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=8
92235 1.37751e-03 92238 9.92357e-05 8016 3.33717e-02 9019 2.95350e-03 1001 6.08364e-02
mix=2 ncm=14
13027 6.03067e-02
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 10.16 18.288 0
cylinder 2 1 10.312 18.288 -.152
unit 2
cuboid 0 1 4p50 50 -.152
hole 1 3r0
hole 1 21.006 2r0
hole 1 -21.006 2r0
hole 1 10.503 18.192 0
hole 1 -10.503 18.192 0
hole 1 10.503 -18.192 0
hole 1 -10.503 -18.192 0
end geom
read array
gbl=1 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 2 end fill
end array
read plot
ttl='hex array' pic=mix lpi=10 scr=yes
xul=0 yul=100 zul=10
xlr=100 ylr=0 zlr=10
uax=1 vdn=-1 nax=400
end plot
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 20 triangular pitched array 7 pins in a circle
read parameters
lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=8
92235 1.37751e-03 92238 9.92357e-05 8016 3.33717e-02 9019 2.95350e-03 1001 6.08364e-02
mix=2 ncm=14
13027 6.03067e-02
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='single cell fuel can in hexprism'
cylinder 10 10.16 18.288 0.0
cylinder 20 10.312 18.288 -0.152
hexprism 30 10.503 18.288 -0.152
media 1 1 10 vol=41514.66537
media 2 1 20 -10 vol=1606.91193
media 0 1 30 -20 vol=6204.469507
boundary 30
unit 2
com='empty cell'
hexprism 10 10.503 18.288 -0.152
media 0 1 10 vol=8155.956715
boundary 10
global unit 3
cylinder 10 31.500 18.288 -0.152
com='7 cylinders in a circle with cylindrical boundary'
array 1 10 place 3 3 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
ara=1 typ=triangular nux=5 nuy=5 nuz=1
fill 7*2 2*1 2*2 3*1 2*2 2*1 7*2 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.21. Sample Problem 21 PARTIALLY FILLED SPHERE
This critical experiment consisted of a partially filled, unreflected spherical container. This aluminum container had an inside diameter of 27.244 in. and a wall thickness of 1/16 in. It is referred to in the report as the 27.3-in.-diameter vessel. The sphere was 98% filled with uranyl fluoride at an enrichment of 4.89% with an H/235U atomic ratio of 1099. The height of the solution in the sphere was 64.6 cm above the bottom of the sphere. A schematic diagram of the apparatus used in the experiment is given in Fig. 8.1.242. The steel tank was ignored.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 21 partially filled sphere
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read geom
global unit 1
hemisphe-z 1 1 34.6 chord 30.
sphere 0 1 34.6
sphere 2 1 34.759
end geom
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=9
1001 6.19770e-02 8016 3.34895e-02 9019 2.50098e-03
92234 2.54224e-07 92235 6.18924e-05 92238 1.18835e-03
mix=2 ncm=14
13027 6.03067e-02
end mixt
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 21 partially filled sphere
read param
lib=4
htm=no
end param
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=9
1001 6.19770e-02 8016 3.34895e-02 9019 2.50098e-03
92234 2.54224e-07 92235 6.18924e-05 92238 1.18835e-03
mix=2 ncm=14
13027 6.03067e-02
end mixt
read geom
global unit 1
sphere 10 34.6 chord -z=30.0
sphere 20 34.6
sphere 30 34.759
media 1 1 10 vol=171309.
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2198.14
media 2 1 30 -20 -10 vol=2403.00
boundary 30
end geom
end data
end
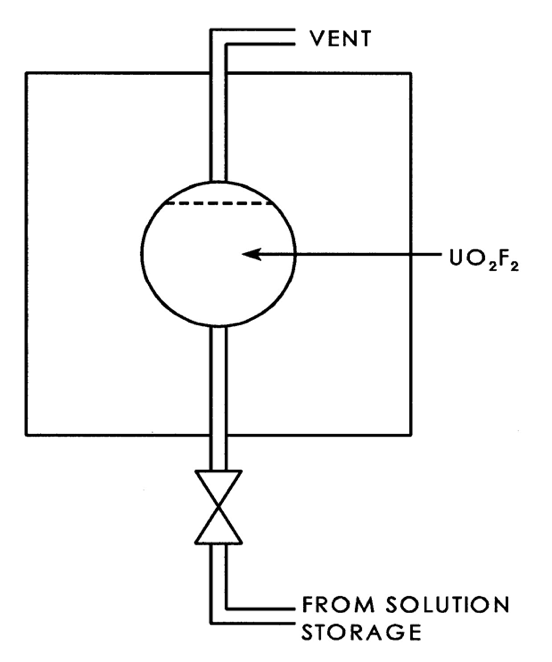
Fig. 8.1.242 Schematic of bare partially filled sphere experiment inside a 9.5-ft-diameter, 9-ft-high steel tank.
8.1.8.3.2.22. Sample Problem 22 CASE 2C8 BARE WITH 3 NESTED HOLES, EACH IS EQUAL VOLUME
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 1. It is a simple 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array of 93.2% wt enriched uranium metal cylinders. This sample problem defines a uranium cylinder in a void spacing cuboid using nested holes. Eight of these units are stacked together in a 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 22 case 2c8 bare with 3 nested, equal volume holes
read parameters
flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 1 1 3.621 2p3.3907
unit 2
cylinder 1 1 4.5622 2p4.2721
hole 1 3*0.0
unit 3
cylinder 1 1 5.2224 2p4.8903
hole 2 3*0.0
unit 4
cylinder 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
hole 3 3*0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
end geometry
read array
nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f4 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 22 case 2c8 bare with 3 nested, equal volume holes
read parameters
flx=yes fdn=yes far=yes gas=no lib=4 mkh=yes ckh=yes fmh=yes
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
cylinder 10 3.621 2p3.3907
media 1 1 10 vol=279.335597542
boundary 10
unit 2
cylinder 20 4.5622 2p4.2721
hole 1
media 1 1 20 vol=279.353142545
boundary 20
unit 3
cylinder 20 5.2224 2p4.8903
hole 2
media 1 1 20 vol=279.333676489
boundary 20
unit 4
cylinder 20 5.748 2p5.3825
cuboid 30 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
hole 3
media 1 1 20 vol=279.34866089
media 0 1 30 -20 vol=1338.755598534
boundary 30
global unit 5
cuboid 10 20.61 -6.87 20.61 -6.87 19.515 -6.505
array 1 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill f4 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.23. Sample Problem 23 CASE 2C8 BARE AS STACKED CYLINDERS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 1. This sample problem describes each of the eight units in the critical 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array using Z hemicylinders (in KENO V.a) or hemicylinders with different chord sizes and directions (in KENO-VI).
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 23 case 2c8 bare as mixed zhemicylinders
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-x half of unit 3'
zhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 0.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 2
com='+x half of unit 3'
zhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 3
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
array 1 3*0.0
unit 4
com='-x portion (more than half) of unit 6'
zhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0
cuboid 0 1 3.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 5
com='+x portion (less than half) of unit 6'
zhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 3.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 6
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
array 2 3*0.0
unit 7
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the -x direction'
zhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 8
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the +x direction'
zhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 9
com='-y half of unit 11'
zhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 0.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 10
com='+y half of unit 11'
zhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505
unit 11
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (zhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 3 3*0.0
unit 12
com='-y portion (more than half) of unit 14'
zhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 3.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 13
com='+y portion (less than half) of unit 14'
zhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 3.0 6.505 -6.505
unit 14
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (zhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 4 3*0.0
unit 15
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the -y direction'
zhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 16
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the +y'
zhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
end geometry
read array
com='array 1 defines unit 3 (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2 defines unit 6 (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3 defines unit 11 (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4 defines unit 14 (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 23 case 2c8 bare as mixed unrotated zcylinders
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-x half of unit 3'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=0.0
cuboid 20 0.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 2
com='+x half of unit 3'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=0.0
cuboid 20 6.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 3
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
array 1 10 place 1 1 1 0.0 0.0 0.0
boundary 10
unit 4
com='-x portion (more than half) of unit 6'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=3.0
cuboid 20 3.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 5
com='+x portion (less than half) of unit 6'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=3.0
cuboid 20 6.87 3.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 6
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
array 2 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
unit 7
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the -x direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=5.748
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 8
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the +x direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=-5.748
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 9
com='-y half of unit 11'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=0.0
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 0.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 10
com='+y half of unit 11'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=0.0
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 11
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
array 3 10 place 1 1 1 0.0 0.0 0.0
boundary 10
unit 12
com='-y portion (more than half) of unit 14'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=3.0
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 3.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 13
com='+y portion (less than half) of unit 14'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=3.0
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.87 3.0 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 14
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
array 4 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
unit 15
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the -y direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=5.748
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 16
com='cylinder of a single zhemicylinder in the +y direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=-5.748
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
global unit 17
cuboid 10 13.74 -13.74 13.74 -13.74 13.010 -13.010
array 5 10 place 1 1 1 -6.87 -6.87 -6.505
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
com='array 1 defines unit 3 (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2 defines unit 6 (zhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3 defines unit 11 (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4 defines unit 14 (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.24. Sample Problem 24 CASE 2C8 BARE AS STACKED ROTATED CYLINDERS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 1. This sample problem describes each of the eight units in the critical 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array using hemicylinders whose axes are in the x direction. In KENO V.a this is realized using xhemicylinders, while in KENO-VI the hemycylinders with different chord sizes are rotated in the X-direction.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 24 case 2c8 bare as mixed xhemicylinders
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-y half of unit 3'
xhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 0.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
unit 2
com='+y half of unit 3'
xhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87
unit 3
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
array 1 3*0.0
unit 4
com='-y portion (more than half) of unit 6'
xhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 3.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
unit 5
com='+y portion (less than half) of unit 6'
xhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 3.0 6.87 -6.87
unit 6
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
array 2 3*0.0
unit 7
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the -y direction'
xhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
unit 8
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the +y direction'
xhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
unit 9
com='-z half of unit 11'
xhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 0.0 -6.87
unit 10
com='+z half of unit 11'
xhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 0.0
unit 11
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 3 3*0.0
unit 12
com='-z portion (more than half) of unit 14'
xhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 3.0 -6.87
unit 13
com='+z portion (less than half) of unit 14'
xhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 3.0
unit 14
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 4 3*0.0
unit 15
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the -z direction'
xhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
unit 16
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the +z direction'
xhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
end geometry
read array
com='array 1 defines unit 3 (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=1 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2 defines unit 6 (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=2 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3 defines unit 11 (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4 defines unit 14 (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 24 case 2c8 bare as mixed x-rotated cylinders
read parameters
rnd=4c6a61962572 npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-y half of unit 3'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=0.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 0.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 2
com='+y half of unit 3'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=0.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 3
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
cuboid 10 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
array 1 10 place 1 1 1 0.0 0.0 0.0
boundary 10
unit 4
com='-y portion (more than half) of unit 6'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=3.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 3.0 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 5
com='+y portion (less than half) of unit 6'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=3.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 3.0 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 6
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
cuboid 10 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
array 2 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
unit 7
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the -y direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=5.748 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 8
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the +y direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=-5.748 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 9
com='-z half of unit 11'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=0.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 0.0 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 10
com='+z half of unit 11'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=0.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 0.0
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 11
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
cuboid 10 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
array 3 10 place 1 1 1 0.0 0.0 0.0
boundary 10
unit 12
com='-z portion (more than half) of unit 14'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=3.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 3.0 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 13
com='+z portion (less than half) of unit 14'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=3.0 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 3.0
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 14
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
cuboid 10 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
array 4 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
unit 15
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the -z direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=5.748 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 16
com='cylinder of a single xhemicylinder in the +z direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=-5.748 rotate a1=90 a2=90
cuboid 20 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
global unit 17
cuboid 10 13.01 -13.01 13.74 -13.74 13.74 -13.74
array 5 10 place 1 1 1 -6.505 -6.87 -6.87
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
com='array 1 defines unit 3 (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=1 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2 defines unit 6 (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
ara=2 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3 defines unit 11 (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4 defines unit 14 (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.25. Sample Problem 25 CASE 2C8 BARE AS MIXED YHEMICYLINDERS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 1. This sample problem describes each of the eight units in the critical 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array using hemicylinders whose axes are in the y direction. This is realized in KENO V.a by using yhemicylinders, while in KENO-VI it is realized using hemicylinders with different chord sizes and directions whose long axes are rotated in the Y-direction.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 25 case 2c8 bare as mixed yhemicylinders
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-x half of unit 3'
yhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 0.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 2
com='+x half of unit 3'
yhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 3
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
array 1 3*0.0
unit 4
com='-x portion (more than half) of unit 6'
yhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0
cuboid 0 1 3.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 5
com='+x portion (less than half) of unit 6'
yhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 3.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 6
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
array 2 3*0.0
unit 7
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the -x direction'
yhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 8
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the +x direction'
yhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 9
com='-z half of unit 11'
yhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 0.0 -6.87
unit 10
com='+z half of unit 11'
yhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 0.0
unit 11
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 3 3*0.0
unit 12
com='-z portion (more than half) of unit 14'
yhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 3.0 -6.87
unit 13
com='+z portion (less than half) of unit 14'
yhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 3.0
unit 14
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 4 3*0.0
unit 15
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the -z direction'
yhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 16
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the +z direction'
yhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
end geometry
read array
com='array 1 defines unit 3 (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2 defines unit 6 (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3 defines unit 11 (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4 defines unit 14 (zhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 25 case 2c8 bare as mixed y-rotated cylinders
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-x half of unit 3'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=0.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 0.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 2
com='+x half of unit 3'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=0.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 3
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
array 1 10 place 1 1 1 0.0 0.0 0.0
boundary 10
unit 4
com='-x portion (more than half) of unit 6'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=3.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 3.0 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 5
com='+x portion (less than half) of unit 6'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=3.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 3.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 6
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
array 2 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
unit 7
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the -x direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -y=5.748 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 8
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the +x direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +y=-5.748 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 9
com='-z half of unit 11'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=0.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 0.0 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 10
com='+z half of unit 11'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=0.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 0.0
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 11
com='cylinder composed of equal halves (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
array 3 10 place 1 1 1 0.0 0.0 0.0
boundary 10
unit 12
com='-z portion (more than half) of unit 14'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=3.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 3.0 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 13
com='+z portion (less than half) of unit 14'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=3.0 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 3.0
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 14
com='cylinder composed of unequal halves (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
cuboid 10 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
array 4 10 place 1 1 1 3*0.0
boundary 10
unit 15
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the -z direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -x=5.748 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
unit 16
com='cylinder of a single yhemicylinder in the +z direction'
cylinder 10 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord +x=-5.748 rotate a1=180 a2=90 a3=90
cuboid 20 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
media 1 1 10 vol=2234.742156
media 0 1 20 -10 vol=2677.511196
boundary 20
global unit 17
cuboid 10 13.74 -13.74 13.01 -13.01 13.74 -13.74
array 5 10 place 1 1 1 -6.87 -6.505 -6.87
boundary 10
end geometry
read array
com='array 1 defines unit 3 (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2 defines unit 6 (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3 defines unit 11 (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4 defines unit 14 (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
read volume
type=random
end volume
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.26. Sample Problem 26 (KENO V.a ONLY) CASE 2C8 BARE AS MIXED ZHEMICYLINDERS WITH ORIGINS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 1. This sample problem describes each of the eight units in the critical 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array using zhemicylinders with origins.
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 26 case 2c8 bare as mixed zhemicylinders with origins
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4 run=yes
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-x half of first cylinder'
zhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 2
com='+x half of first cylinder'
zhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 6.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 3
com='1st cylinder composed of equal portions (z hemicylinders with x radii)'
array 1 3*0.0
unit 4
com='-x portion (more than half) of second cylinder'
zhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 9.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 5
com='+x portion (less than half) of second cylinder'
zhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 9.87 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 6
com='2nd cylinder composed of unequal portions (z hemicylinders with x radii)'
array 2 3*0.0
unit 7
com='3rd cylinder: described as a zhemicylinder in the -x direction'
zhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 0.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 8
com='4th cylinder: described as a zhemicylinder in the +x direction'
zhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 0.0 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 9
com='-y half of fifth cylinder'
zhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505
unit 10
com='+y half of fifth cylinder'
zhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 13.74 6.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 11
com='5th cylinder composed of equal portions (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
array 3 3*0.0
unit 12
com='-y portion (more than half) of sixth cylinder'
zhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 9.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505
unit 13
com='+y portion (less than half) of sixth cylinder'
zhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 13.74 9.87 6.505 -6.505
unit 14
com='6th cylinder composed of unequal portions (zhemicylinders with y radii)'
array 4 3*0.0
unit 15
com='7th cylinder: described as a zhemicylinder in the -y direction'
zhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 13.74 0.0 6.505 -6.505
unit 16
com='8th cylinder: described as a zhemicylinder in the +y direction'
zhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 13.74 0.0 6.505 -6.505
global unit 17
com='complete 2c8 bare configuration'
array 5 3*0.0
end geometry
read array
com='array 1: 1st cylinder (unit 3) equal x portions of zhemicylinders'
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2: 2nd cylinder (unit 6) unequal x portions of zhemicylinders'
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3: 5th cylinder (unit 11) equal y portions of zhemicylinders'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4: 6th cylinder (unit 14) unequal y portions of zhemicylinders'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.27. Sample Problem 27 (KENO V.a oONLY) CASE 2C8 BARE AS MIXED XHEMICYLINDERS WITH ORIGINS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 1. This sample problem describes each of the eight units in the critical 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array using hemicylinders whose axes are in the x direction. Origins are specified for each hemicylinder.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 27 case 2c8 bare as mixed xhemicylinders with origins
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4 run=yes
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-y half of first cylinder'
xhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87
unit 2
com='+y half of first cylinder'
xhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 13.74 6.87 6.87 -6.87
unit 3
com='1st cylinder composed of equal portions (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
array 1 3*0.0
unit 4
com='-y portion (more than half) of second cylinder'
xhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 9.87 0.0 6.87 -6.87
unit 5
com='+y portion (less than half) of second cylinder'
xhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 13.74 9.87 6.87 -6.87
unit 6
com='2nd cylinder composed of unequal portions (xhemicylinders with y radii)'
array 2 3*0.0
unit 7
com='3rd cylinder: described as a xhemicylinder in the -y direction'
xhemicyl-y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 13.74 0.0 6.87 -6.87
unit 8
com='4th cylinder: described as a xhemicylinder in the +y direction'
xhemicyl+y 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 13.74 0.0 6.87 -6.87
unit 9
com='-z half of fifth cylinder'
xhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 6.87 0.0
unit 10
com='+z half of fifth cylinder'
xhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 13.74 6.87
unit 11
com='5th cylinder composed of equal portions (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 3 3*0.0
unit 12
com='-z portion (more than half) of sixth cylinder'
xhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 9.87 0.0
unit 13
com='+z portion (less than half) of sixth cylinder'
xhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 13.74 9.87
unit 14
com='6th cylinder composed of unequal portions (xhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 4 3*0.0
unit 15
com='7th cylinder: described as a xhemicylinder in the -z direction'
xhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 13.74 0.0
unit 16
com='8th cylinder: de3scribed as a xhemicylinder in the +z direction'
xhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87 13.74 0.0
global unit 17
com='complete 2c8 bare configuration'
array 5 3*0.0
end geometry
read array
com='array 1: 1st cylinder (unit 3) equal y portions of xhemicylinders'
ara=1 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2: 2nd cylinder (unit 6) unequal y portions of xhemicylinders'
ara=2 nux=1 nuy=2 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3: 5th cylinder (unit 11) equal z portions of xhemicylinders'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4: 6th cylinder (unit 14) unequal z portions of xhemicylinders'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.28. Sample Problem 28 (KENO V.a oONLY) CASE 2C8 BARE AS MIXED YHEMICYLINDERS WITH ORIGINS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 1. This sample problem describes each of the eight units in the critical 2 \(\times\) 2 \(\times\) 2 array using hemicylinders whose axes are in the y direction. Origins are specified for each hemicylinder.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 28 case 2c8 bare as mixed yhemicylinders with origins
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4 run=yes
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=1
92234 4.82717e-04 92235 4.47971e-02 92236 9.57233e-05 92238 2.65767e-03
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
com='-x half of first cylinder'
yhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 6.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 2
com='+x half of unit 3'
yhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 3
com='1st cylinder composed of equal portions (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
array 1 3*0.0
unit 4
com='-x portion (more than half) of second cylinder'
yhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 9.87 0.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 5
com='+x portion (less than half) of second cylinder'
yhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 9.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 6
com='2nd cylinder composed of unequal portions (yhemicylinders with x radii)'
array 2 3*0.0
unit 7
com='3rd cylinder: described as a single yhemicylinder in the -x direction'
yhemicyl-x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 0.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 8
com='4th cylinder: described as a single yhemicylinder in the +x direction'
yhemicyl+x 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 6.87 0.0
cuboid 0 1 13.74 0.0 6.505 -6.505 6.87 -6.87
unit 9
com='-z half of fifth cylinder'
yhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 6.87 0.0
unit 10
com='+z half of sixth cylinder'
yhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 13.74 6.87
unit 11
com='5th cylinder composed of equal portions (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 3 3*0.0
unit 12
com='-z portion (more than half) of sixth cylinder'
yhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 3.0 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 9.87 0.0
unit 13
com='+z portion (less than half) of sixth cylinder'
yhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord -3.0 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 13.74 9.87
unit 14
com='6th cylinder composed of unequal portions (yhemicylinders with z radii)'
array 4 3*0.0
unit 15
com='7th cylinder: described as a yhemicylinder in the -z direction'
yhemicyl-z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 13.74 0.0
unit 16
com='8th cylinder: described as a yhemicylinder in the +z direction'
yhemicyl+z 1 1 5.748 5.3825 -5.3825 chord 5.748 origin 0.0 6.87
cuboid 0 1 6.87 -6.87 6.505 -6.505 13.74 0.0
global unit 17
com='complete 2c8 bare configuration'
array 5 3*0.0
end geometry
read array
com='array 1: 1st cylinder (unit 3) equal x portions of yhemicylinders'
ara=1 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 1 2 end fill
com='array 2: 2nd cylinder (unit 6) unequal x portions of yhemicylinders'
ara=2 nux=2 nuy=1 nuz=1 fill 4 5 end fill
com='array 3: 5th cyllinder (unit 11) equal z portions of yhemicylinders'
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 9 10 end fill
com='array 4: 6th cylinder (unit 14) unequal z portions of yhemicylinders'
ara=4 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 12 13 end fill
com='array 5 defines the total 2c8 problem'
gbl=5 ara=5 nux=2 nuy=2 nuz=2 fill 3 7 6 8 11 15 14 16 end fill
end array
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.29. Sample Problem 29 BARE CRITICAL SPHERE 3.4420-IN. RADIUS
This problem is a critical experiment [KENO-Appendix-CMLTH93] consisting of a critical Oralloy sphere. The density of the Oralloy is 18.747 g/cc, and the isotopic enrichment (wt %) is 93.21% 235U, 5.7697% 238U, 0.9844% 234U, and 0.0359% 236U. The critical radius was 8.74268 cm. A photograph of the experiment is given in Fig. 8.1.243. The support structure was ignored in the input data.
Fig. 8.1.243 Critical Oralloy sphere.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 29 bare critical sphere 3.4420" radius
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=16 ncm=16
92235 4.47709e-02 92238 2.73631e-03 92234 4.74858e-04 92236 1.71704e-05
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
sphere 16 1 8.74268
end geometry
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
ttl='x-y slice at z=0.0'
xul=-9 yul= 9 zul=0.0
xlr= 9 ylr=-9 zlr=0.0
uax=1 vdn=-1 nax=400 nch=' *'
end plot
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 26 bare critical sphere 3.4420" radius
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=16
92235 4.47709e-02
92238 2.73631e-03
92234 4.74858e-04
92236 1.71704e-05
end mixt
read geometry
global unit 1
sphere 10 8.74268
media 1 1 10 vol=2799.1254126
boundary 10
end geometry
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.30. Sample Problem 30 (KENO V.a ONLY) BARE CRITICAL SPHERE Z HEMISPHERE MODEL 3.4420-IN. RADIUS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 29. This sample problem describes the sphere as two Z hemispheres, each with a chord and origin specified. One of the hemispheres is placed using the hole geometry option.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 30 bare critical sphere z hemisphere model 3.4420" radius
read parameters
npg=1000 fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=16
92235 4.47709e-02 92238 2.73631e-03 92234 4.74858e-04 92236 1.71704e-05
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
hemisphe+z 16 1 8.74268 chord +3.0 origin 8.9 8.9 8.9
global unit 2
hemisphe-z 16 1 8.74268 chord -3.0 origin 8.9 8.9 8.9
cuboid 0 1 17.8 0.0 17.8 0.0 17.8 0.0
hole 1 3*0.0
end geometry
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
ttl='y-z slice at x=8.9 mixture map'
xul=8.9 yul=-0.5 zul=18.5
xlr=8.9 ylr=18.5 zlr=-0.5
vax=1 wdn=-1 nax=400 end plt1
ttl='y-z slice at x=8.9 unit map'
pic=unit end plt2
end plot
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.31. Sample Problem 31 (KENO V.a ONLY) BARE CRITICAL SPHERE X HEMISPHERE MODEL 3.4420-IN. RADIUS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 29. This sample problem describes the sphere as two X hemispheres, each with a chord and origin specified. One of the hemispheres is placed using the hole geometry option.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 31 bare critical sphere x hemisphere model 3.4420" radius
read parameters
fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=16 ncm=16
92235 4.47709e-02 92238 2.73631e-03 92234 4.74858e-04 92236 1.71704e-05
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
hemisphe-x 16 1 8.74268 chord +3.0
global unit 2
hemisphe+x 16 1 8.74268 chord -3.0 origin 8.9 8.9 8.9
cuboid 0 1 17.8 0.0 17.8 0.0 17.8 0.0
hole 1 3*8.9
end geometry
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
ttl='x-y slice at z=8.9 mixture map'
xul=-0.5 yul=18.5 zul=8.9
xlr=18.5 ylr=-0.5 zlr=8.9
uax=1 vdn=-1 nax=400 end plt1
ttl='y-z slice at x=8.9 unit map'
pic=unit end plt2
end plot
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.32. Sample Problem 32 (KENO V.a ONLY) BARE CRITICAL SPHERE Y HEMISPHERE MODEL 3.4420-IN. RADIUS
The physical representation of this sample problem is the critical experiment described in sample problem 29. This sample problem describes the sphere as two Y hemispheres, each with a chord and origin specified. One of the hemispheres is placed using the hole geometry option.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 32 bare critical sphere y hemisphere model 3.4420" radius
read parameters
fdn=yes lib=4
htm=no
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=16 ncm=16
92235 4.47709e-02 92238 2.73631e-03 92234 4.74858e-04 92236 1.71704e-05
end mixt
read geometry
unit 1
hemisphe-y 16 1 8.74268 chord +3.0 origin 8.9 9.9 10.9
global unit 2
hemisphe+y 16 1 8.74268 chord -3.0 origin 8.9 8.9 8.9
cuboid 0 1 17.8 0.0 17.8 0.0 17.8 0.0
hole 1 0.0 -1.0 -2.0
end geometry
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
ttl='x-y slice at z=8.9 mixture map'
xul=-0.5 yul=18.5 zul=8.9
xlr=18.5 ylr=-0.5 zlr=8.9
uax=1 vdn=-1 nax=400 end plt1
ttl='y-z slice at x=8.9 unit map'
pic=unit end plt2
end plot
end data
end
8.1.8.3.2.33. Sample Problem 33 CRITICAL TRIANGULAR PITCHED ARRAY OF ANNULAR RODS
This sample problem represents a critical experiment [KENO-Appendix-CJoh66] that consists of a partially flooded array of 19 low enriched uranium metal cylindrical annuli billets arranged in a triangular pitched array. The density of the uranium metal was 19.0 g/cc, and the isotopic enrichment in weight percent was 1.95% 235U, 98.02% 238U, 0.006% 236U, and 0.002% 234U. The cylindrical annuli had an inside diameter of 6.604 cm, an outside diameter of 18.288 cm, and were placed with a pitch of 20.828 cm. Each billet was 101.6 cm long. The array was positioned in a very large tank. This configuration was critical when the tank was filled to a height of 47.7 cm on a scale whose zero point was 0.6 cm below the bottom of the billets. The bottom of the billets was 21.6 cm above the bottom of the tank. The tank and all support structures have been ignored in this model. The model utilizes only 15.24 cm of water reflector on all sides of the array. Fig. 8.1.244 and Fig. 8.1.245 provide a representation of the model. A photograph of a single annular billet is shown in Fig. 8.1.246.
Input Data
KENO V.a
=kenova
sample problem 33 critical triangular pitched array of annular rods
read parameters fdn=yes nub=yes lib=4
htm=no npg=2000
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=17 ncm=17
92235 9.49270e-04 92238 4.71245e-02 92234 9.77785e-07 92236 2.90844e-06
mix=18 ncm=18
8016 3.33757e-02 1001 6.67515e-02
mix=19 ncm=19
1001 6.67515e-02 8016 3.33757e-02
mix=20 ncm=20
92235 9.49270e-04 92238 4.71245e-02 92234 9.77785e-07 92236 2.90844e-06
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
zhemicyl-x 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6
zhemicyl-x 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6
unit 2
zhemicyl-y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6
zhemicyl-y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6
unit 3
zhemicyl+x 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6
zhemicyl+x 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6
unit 4
zhemicyl+y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 -18.03758
zhemicyl+y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 -18.03758
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 47.7 0.6
hole 1 10.414 0.0 0.0
hole 2 0.0 18.03758 0.0
hole 3 -10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 5
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 10.414 0.0 47.7 0.6
unit 6
zhemicyl-y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6
zhemicyl-y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 0.0 -10.414 47.7 0.6
unit 7
zhemicyl-y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 18.03758
zhemicyl-y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 18.03758
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 47.7 0.6
hole 3 -10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 8
zhemicyl+y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 -18.03758
zhemicyl+y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 -18.03758
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 47.7 0.6
hole 3 -10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 9
zhemicyl+y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6
zhemicyl+y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 10.414 0.0 47.7 0.6
unit 10
zhemicyl+y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 -18.03758
zhemicyl+y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 -18.03758
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 47.7 0.6
hole 1 10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 11
zhemicyl-y 18 1 3.302 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 18.03758
zhemicyl-y 17 1 9.144 47.7 0.6 origin 0.0 18.03758
cuboid 19 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 47.7 0.6
hole 1 10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 21
zhemicyl-x 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7
zhemicyl-x 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7
unit 22
zhemicyl-y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7
zhemicyl-y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7
unit 23
zhemicyl+x 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7
zhemicyl+x 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7
unit 24
zhemicyl+y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 -18.03758
zhemicyl+y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 -18.03758
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 102.2 47.7
hole 21 10.414 0.0 0.0
hole 22 0.0 18.03758 0.0
hole 23 -10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 25
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 10.414 0.0 102.2 47.7
unit 26
zhemicyl-y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7
zhemicyl-y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 0.0 -10.414 102.2 47.7
unit 27
zhemicyl-y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 18.03758
zhemicyl-y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 18.03758
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 102.2 47.7
hole 23 -10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 28
zhemicyl+y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 -18.03758
zhemicyl+y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 -18.03758
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 102.2 47.7
hole 23 -10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 29
zhemicyl+y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7
zhemicyl+y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 10.414 0.0 102.2 47.7
unit 30
zhemicyl+y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 -18.03758
zhemicyl+y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 -18.03758
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 102.2 47.7
hole 21 10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 31
zhemicyl-y 0 1 3.302 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 18.03758
zhemicyl-y 20 1 9.144 102.2 47.7 origin 0.0 18.03758
cuboid 0 1 2p10.414 2p18.03758 102.2 47.7
hole 21 10.414 0.0 0.0
unit 32
com='flooded portion of array with 15.24 cm of water in x and y'
array 1 2*0.0 0.6
replicate 19 1 4r15.24 0.0 0.6 1
replicate 19 2 5r0.0 3.0 7
unit 33
com='unflooded upper portion of array'
array 2 3*0.0
replicate 0 1 4r15.24 2*0.0 1
global
unit 34
array 3 -67.31 -61.72916 -21.0
end geom
read bias
id=500 2 8
end bias
read array
ara=1 nux=5 nuy=4 nuz=1 fill 5 3r 6 5 11 3r 4 7 10 3r 4 8 5 3r 9 5 end fill
ara=2 nux=5 nuy=4 nuz=1 fill 25 3r26 25 31 3r24 27 30 3r24 28 25 3r29 25 end fill
ara=3 nux=1 nuy=1 nuz=2 fill 32 33 end fill
end array
read start
nst=1 xsm=-52 xsp=52 ysm=-47 ysp=47 zsm=0.6 zsp=47.7
end start
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
clr=17 255 0 0
18 128 255 255
19 0 0 255
20 255 0 128
end color
ttl='x-y plot of pins at z=45.0'
xul=-52.0 yul= 47.0 zul=45.0
xlr= 52.0 ylr=-47.0 zlr=45.0
uax= 1.0 vdn=-1.0 nax=400
end plt1
ttl='x-z plot of pins at y=0.0'
xul=-52.0 yul=0.0 zul=102.7
xlr= 52.0 ylr=0.0 zlr=-3.0
uax= 1.0 wdn=-1.0 nax=400
end plt2
ttl='x-z plot at y=0.0'
xul=-68.0 yul=0.0 zul=102.7
xlr= 70.0 ylr=0.0 zlr=-25.0
uax= 1.0 wdn=-1.0 nax=400
end plt3
end plot
end data
end
KENO-VI
=kenovi
sample problem 27 critical triangular pitched array of annular rods
read parameters
fdn=yes nub=yes lib=4
htm=no
npg=4000
end parameters
read mixt
sct=2
mix=1 ncm=17
92235 9.49270e-04
92238 4.71245e-02
92234 9.77785e-07
92236 2.90844e-06
mix=2 ncm=18
8016 3.33757e-02
1001 6.67515e-02
mix=3 ncm=19
1001 6.67515e-02
8016 3.33757e-02
mix=4 ncm=20
92235 9.49270e-04
92238 4.71245e-02
92234 9.77785e-07
92236 2.90844e-06
mix=5 ncm=18
8016 3.33757e-02
1001 6.67515e-02
end mixt
read geom
unit 1
cylinder 10 3.302 102.2 0.6
cylinder 20 9.144 102.2 0.6
plane 30 zpl=1.0 con=-47.7
hexprism 40 10.414 102.2 0.0
media 2 1 10 -30
media 1 1 20 -10 -30
media 3 1 40 -20 -30
media 0 1 10 30
media 4 1 20 -10 30
media 0 1 40 -20 30
boundary 40
unit 2
plane 10 zpl=1.0 con=-47.7
hexprism 20 10.414 102.2 0.0
media 3 1 -10 20
media 0 1 10 20
boundary 20
global unit 3
cylinder 10 52.42 102.2 0.0
plane 20 zpl=1.0 con=-47.7
cylinder 30 82.9 102.2 -21.0
array 1 10 place 4 4 1 3*0.0
media 0 1 30 20 -10
media 5 1 30 -20 -10
boundary 30
end geom
read array
ara=1 nux=7 nuy=7 nuz=1 typ=tri fill
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2 2 1 1 1 2
2 2 1 1 1 1 2
2 1 1 1 1 1 2
2 1 1 1 1 2 2
2 1 1 1 2 2 2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 end fill
end array
read volume
type=random
end volume
read plot
scr=yes lpi=10
clr=1 255 0 0
2 128 255 255
3 0 0 255
4 255 0 128
5 200 200 200
end color
ttl='x-z plot of pins at y=0.0'
xul=-68.0 yul= 0.0 zul=102.7
xlr= 70.0 ylr= 0.0 zlr=-25.0
uax= 1.0 wdn=-1.0
nax=800
end plt0
ttl='x-y plot of pins and water at z=45.0'
xul=-68.0 yul= 68.0 zul=45.0
xlr= 68.0 ylr=-68.0 zlr=45.0
uax= 1.0 vdn= -1.0
nax=800
end plt1
end plot
end data
end
Fig. 8.1.244 Horizontal slice through a critical triangular pitched array of partially flooded 1.95% enriched uranium metal annular billets.
Fig. 8.1.245 Vertical slice through the center of a critical triangular-pitched array of partially flooded 1.9% enriched uranium metal annular billets.
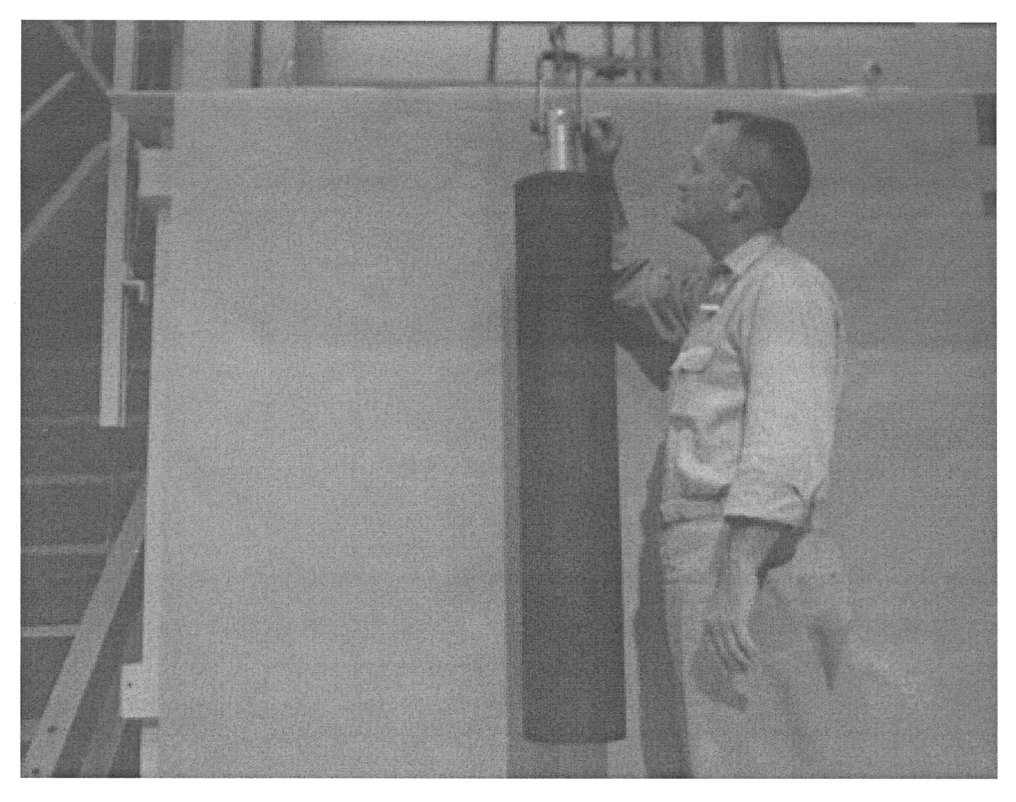
Fig. 8.1.246 1.95% Enriched uranium metal annular billet used in critical experiments
References
- KENO-Appendix-CBKH+77
Clco C. Byers, Jerry J. Koelling, Gordon E. Hansen, David R. Smith, and Howard R. Dyer. Critical measurements of a water-reflected enriched uranium sphere. In Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, volume 27. 1977.
- KENO-Appendix-CIM64
D. C. Irving and John T. Mihalczo. Monte Carlo Calculations for Enriched Uranium Metal Assemblies. In Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, volume 7. 1964.
- KENO-Appendix-CJoh66
E. B. Johnson. Critical Parameters of Uranium (1.95) Metal Cylindrical Annuli. In Transactions of the American Nuclear Society, volume 9. 1966.
- KENO-Appendix-CMLTH93
J. T. Mihalczo, J. J. Lynn, J. R. Taylor, and G. E. Hansen. Measurements with an unreflected uranium (93.2%) metal sphere. Technical Report, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN (USA), 1993.
- KENO-Appendix-CTho64
J. T. Thomas. CRITICAL THREE-DIMENSIONAL ARRAYS OF NEUTRON-INTERACTING UNITS. PART II. U (93.2) METAL. Technical Report, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, TN (USA), 1964.
- KENO-Appendix-CTho73
Joseph T. Thomas. Critical three-dimensional arrays of U (93.2)-metal cylinders. Nuclear Science and Engineering, 52(3):350–359, 1973. Publisher: Taylor & Francis.
- KENO-Appendix-CWT69
G. E. Whitesides and J. T. Thomas. USE OF DIFFERENTIAL CURRENT ALBEDOS IN MONTE CARLO CRITICALITY CALCULATIONS. Technical Report, Union Carbide Corp., Oak Ridge, Tenn., 1969.